Resume vs. CV: Key Differences Explained
May 29 2025
Most people use the resume and CV (Curriculum Vitae) interchangeably. They do have some things in common, but there are also a few differences between a resume and a CV. Believe it or not, even employers and recruiters use them, thinking they’re the same thing.
Whether you’re going for a position abroad or just a local business, this kind of conflicting data can push you in the wrong direction.
Sending one when you need the other could cost you the interview. With these thoughts in mind, here’s what makes a good resume and the differences between them.
What’s a Resume?
A resume is practically a piece of content including abstract information about yourself. It comes from French and summarizes your history in terms of education, career, and relevant skills. All these things are provided in reverse chronological order, so you need to start with your latest jobs.
Additional sections, such as personal or volunteer work, can also be included. Some applicants may also include relevant hobbies.
What’s the CV (Curriculum Vitae) About Then?
The CV stands for curriculum vitae. In free translation from Latin, it’s meant to provide details about your life.
It’s longer than a resume. It includes more details about your experience if you’ve attended a secondary school.
It’s supposed to be much longer than a resume, as it includes more data about your work and education. However, just like the resume, it should be spot on.
Based on the type of CV, it could be much longer than a traditional resume.
For example, an academic CV is meant to include more information than a CV for a sales job. Such a position is more competitive, so you must include more than just a few bits. Academic CVs must include research studies, publications, awards, and other similar things to attract recruiters.
The Geographical Approach
Think about where you’d like to work.
The job you go for can definitely dictate what you need, but the location is just as important. In the USA, a resume rarely has more than a couple of pages. It covers around 10-15 years of your past work experience.
The CV is sometimes referred to as being academic. It’s a common requirement for highly competitive jobs and academic positions. Most of these jobs require secondary education, too.
If you apply for a job in the UK (being a local or applying for jobs abroad), a traditional employment CV is similar to the resume in the USA. Of course, the academic one could be much longer and may go as long as 10 pages.
Comparison and Difference Between Resume and CV Format
When not sure what makes a good resume, you’ll need to ensure that you first understand how resumes and CVs work. Furthermore, a service like CraftResumes can help you reach your goals by compiling all the information professionally.
You know better than anyone else where you’ve worked and what you’ve done, but professional writers can make a resume look more appealing. Besides, expert resume writers often have a background in recruitment, so they’ll know what draws a recruiter’s attention.
Differences in What the Content Emphasizes
A resume is focused on your experience in the working field. Your personal skills will also be among the priorities. On the other hand, a CV emphasizes academic achievements more. It’s mainly about research studies, superior education, and highly competitive jobs.
Differences in Industries and Applications
A resume can be used to apply for any job. You can have a resume to apply for a cleaning job, warehouse work, or accounting, just to give you a few examples. The CV is more appropriate for positions that require superior education, such as academic positions based on faculty degrees.
Differences in Length
It’s an unwritten rule, but resumes usually have one or two pages, not more. Sure, some exceptions exist, such as jobs held for long periods or career gaps. When it comes to a CV, the length may vary. There are no limits here. Two pages could do, but you can have three or four pages, even up to 10.
Differences in the Background
According to your education, you can choose between a CV and a resume, yet it’s better to seek clarification if you’re unsure. A CV is more suitable for academic roles like education or research. The resume can be used for any other job opportunity.
Regarding the actual content, resumes and CVs have pretty much the same sections.
Plus, sections can be removed if irrelevant to the job application. They can also be taken off with time, since you should advance in your career.
The resume objective is an introduction to your skills. The CV is more comprehensive and includes much more data.
How to Choose Between a Resume and a Curriculum Vitae?
Deciding on the right introduction is pretty simple once you get the difference between a resume and a CV.
Then, if you end up talking to a recruiter and they require more info, it’s essential to know when to choose one or the other.
What Job do You Apply For?
Applying for an academic role will usually require a CV. It should be an academic CV. On the other hand, applying for other types of jobs will require a resume. Some institutions or companies make sure to provide guidelines regarding their requirements, so you’ll know what to include.
Where is the Company Located?
Applying for a local job could simplify it, as now you know when to use a resume and when to rely on a comprehensive CV. Applying for a job abroad could be more complicated because different jurisdictions have different names. In some countries, a resume and a CV are the same thing.
Here are a few things to keep in mind for guidance:
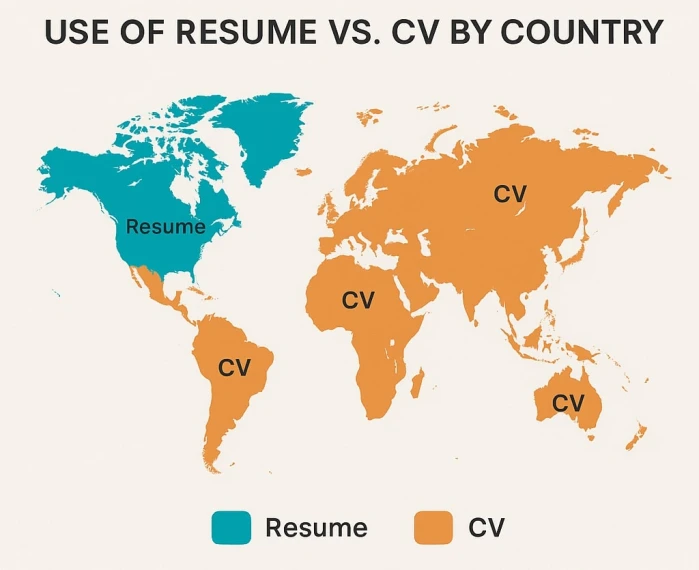
- In India, Australia, and South America, a resume and a CV refer to the same thing.
- In many European countries, most employers will ask for CVs, yet they’re often drafted like resumes, based on the job.
- In New Zealand, Ireland, or the UK, you’ll usually be asked for an employment CV.
- In the USA and Canada, CVs are required for academic jobs, while most other jobs will do with resumes.
Once again, pay attention to the recruiter’s instructions, as they may provide details about the requirements.

A Few Tips and Tricks to Meet the Resume Objective
Knowing the difference between a resume and a CV, or what makes a good resume, isn’t everything. Here are a few tips to write your resume if you decide to take a chance and write it yourself.
Tailor It to the Job
No matter what role you apply for, the resume or CV should be tailored for it. The recruiter must understand how your experience aligns with the job. Highlight important and relevant tasks, rather than unrelated responsibilities that won’t make any difference whatsoever.
Results Over Responsibilities
While duties are important, most people fail to showcase their results as well. Instead, they focus on their responsibilities only. While they also matter, you must show a recruiter that you’ve achieved specific goals in your previous positions. Offering tangible information can show a recruiter how you can help the institution or company.
Double-check Spelling and Grammar
Spelling, grammar, and punctuation must be perfect. This is even more important if you apply for a position abroad. Just because you can use English, it doesn’t mean spelling and grammar are identical. If you live in the United States and apply for a job in the UK, use British English to write your resume.
Ask for Help
You probably know better what working experience you’ve had. True, but then, many suitable candidates are rejected because their resumes are poorly written. You may ask for a second or third opinion, or even better, get a professional service to do it for you.
Conclusion
In the end, there are quite a few differences between these papers. However, job responsibilities are the main difference between a resume and a CV. Of course, applying for a job overseas could require more attention. There are other small bits you should consider.
Most recruiters mention whether they want a resume or a CV in the job description. What makes a good resume is probably more important in the attempt to secure the perfect job, so think about other aspects as well, such as the length, customization, and a format that’s very easy to read and straightforward.
